
MARINE RIPRAP COFFERDAM COPOSITE WATER-STOPPING REINFORCEMENT GROUTING
Coastal curtain grouting technology
1. Project Background
With the addition of generating units at a coastal thermal power plant, it was planned to build a large aeration tank and waste water cooling discharge channel between two riprap seawalls.
Due to engineering needs, a closed impervious cofferdam had to be installed between the coastal seawalls to facilitate subsequent drainage of the seawater in the cofferdam for the construction of the aeration tank structure.
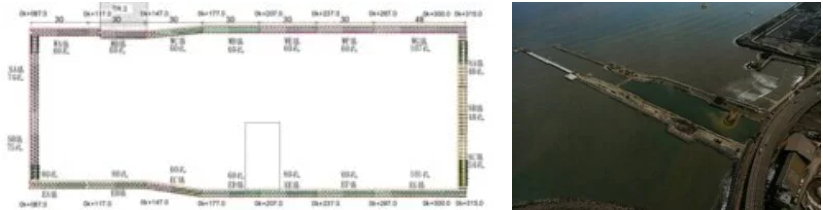
The scale of the cofferdam was about 230m (length) × 90m (width) × 12m (depth). Because of the extremely large voids of the riprap seawall, coupled with the influence of factors such as tides, marine conditions, drifting sand, and seawater salinity, traditional grouting methods would not have achieved the function of blocking the influx of seawater into the cofferdam.
In order to overcome construction difficulties, the contractor specially invited professional manufacturers to discuss suitable plugging methods, so that the project could proceed smoothly.
―
2. Solution
After detailed evaluation by experts from various fields, it was decided to construct four water-stop curtains deep into the sea bed using the riprap on the side facing the sea and composite grouting technology on the inner side of the seawall.
At the same time, the dual effects of blocking the influx of seawater into the construction site and strengthening the seabed would be achieved. The relevant planning schemes was as follows:
(1) The adoption of salt-alkali-resistant long-lasting grouting material to ensure the long-term water stop function of the seawall.
(2) Above and below the interface impacted by tides and waves are configured with grout of different properties to ensure the effect of void filling.
(3) From the bottom of the cofferdam to the sandy seabed fresh rock plate, the compaction double-tube grouting method to be adopted to achieve the purpose of reducing leakage and preventing drifting sand.
(4) The permeability coefficient (k) of the water-stop curtain after grouting is not to be greater than 1×10-5cm/sec, which is in line with the condition of using a temporary water pump to immediately remove the infiltration of seawater during construction.
(5) The grouting operation shall be completed within four months, and the equipment and tools during the construction process shall not affect the passage of other engineering vehicles on the seawall.

―
3. Works Design
In order to meet the long-term use of the cofferdam in the future, the grouting design adopted long-term water-stopping and reinforcement functions. The plan was as follows:
(1) For the underwater riprap layer, use salt-alkali-resistant long-acting quick-setting cement grouting technology (FLW Grouting) to control the curing time from 5 ~ 120 seconds, and adjust it appropriately according to the void condition of the riprap layer.
(2) For the areas affected by waves and tides on the above water riprap layer, use Visco Top Grouting technology and control the curing time within 30 minutes, and adjust appropriately according to the tide and marine conditions.
(3) The FLW grout is sandwiched between the underwater riprap layers, similar to dam core design, and the modified hot bitumen grouting technology (Hot Bitumen Grouting) is used to fill voids that are not penetrated by the FLW grout and Visco grout. The main condition of the grout material is that the viscosity is not less than 14000cps at 80 degrees Celsius.
(4) Water-stop grouting is carried out for the cracks in the rock plate and the seabed, so that the seawater will not penetrate into the cofferdam through the sand layer under the seawall.
Use Double Packer Grouting technology with SSA long-lasting chemical grout and CB grout for penetration and compaction pouring, control the gel time to 15-60 seconds, and adjust it according to the water permeability and void conditions of the seabed.

―
4. Works Process
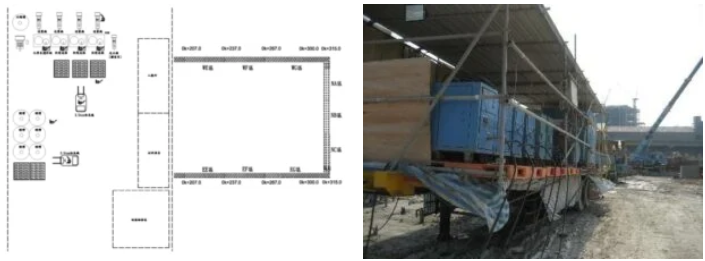
In order to save work time and avoid placing construction equipment in the embankment top passageway, the on-site configuration adopted the independent operations of drilling, mixing, pipeline, and pouring as follows:
(1) Drill holes and pre-embed multiple grouting pipes at corresponding locations on site according to the design drawings.
(2) Mixing area set up at a location that did not affect the passage of vehicles, and place all materials and mixing equipment in this area.
(3) Grout delivery pipes were set in advance, and grout outlet and switch valves were placed near the filling hole.
(4) The grouting machine, slow mixer, power unit and automatic pressure and flow monitoring equipment, etc., were installed on independent vehicles according to the different types of grout materials.
(5) During the grouting operation, the material was uniformly supplied by the mixing area. After each grouting vehicle was connected to the grouting outlet at the proximal end of the hole position, the grouting machine on the vehicle started operation.
This achieved the advantages of time and space of mobile pouring of different grouting materials, rapid movement, and instant supplementary grouting.
―
5. Results
In order to seal the voids of the riprap seawall and reduce the water permeability of the seabed, so the subsequent projects could proceed smoothly, grouting results quality control was adopted: early ground resistance detection, water level observation inside/outside the cofferdam, on-site permeation testing, ground resistance detection after pouring, ground penetrating radar detection, test pit excavation inspection and other methods were used for multiple testing.
Multiple inspections were carried out by methods such as inspection of test pit excavation. After repeated supplementary grouting and inspection operations for possible defective locations, and after confirming that uncertain factors had been completely eliminated, the staged excavation was carried out.
After excavation, it was found that the amount of water permeating into the cofferdam per hour was less than 0.5m3. This could be removed completely by the guide trench inside the cofferdam and the pump.
In accordance with the construction requirements of subsequent structures, the composite water-stopping reinforcement grouting work of the marine riprap cofferdam was successfully completed.

―
Marine Riprap Cofferdam Composite Water-Stopping Reinforcement Grouting
將下載檔案寄至:
・More Construction Result Sharing
Contact us:+886 2769-2355
Copyright ©Jines Construction Co.,Ltd