
BASE LEVEL GROUT SEALING OF DEEP EXCAVATION IN COASTAL TIDAL ZONE
Water-stop grouting site improvement technology for base level excavation in saline-alkali area
—
1. Project Background
A proposed ecological landscape-based seawater supply system was planned to be constructed in a coastal tidal zone. It involved the construction of work shafts and diversion channels.
However, the proximity of the site to the coastline, coupled with the presence of highly permeable silty sand with gravel layers within the excavation depth, hindered effective dewatering during the excavation process.
This resulted in significant impact on the project’s progress. To facilitate smooth project advancement, the contracting authority commissioned a professional firm to develop a subgrade grouting solution to prevent further groundwater intrusion.

—
2. Solution
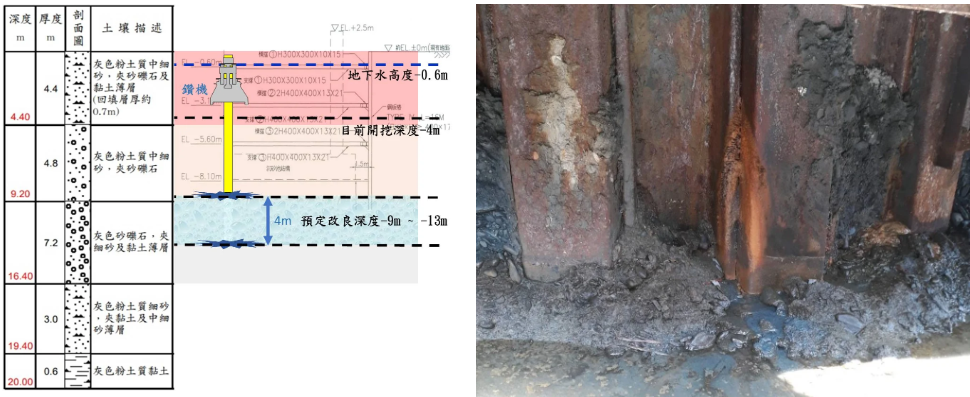
The proposed excavation for this project had an approximate depth of GL-8.1m. The soil retention system consisted of steel sheet piles with internal bracing design.
The steel sheet piles penetrated a layer of sand, gravel, and fine sand, along with a thin layer of clay, extending approximately 2m below the excavation face.
However, noticeable groundwater seepage occurred in the excavation face, below the soil retention system, and within the gaps of the steel sheet piles when the excavation reached around GL-4.0m.
To continue with the excavation, the following solution was proposed:
- Implement base level grouting to reduce the permeability of the soil beneath the soil retention system and excavation face.
- Use instant and delayed setting grout materials to fill and seal the voids within the granular soil.
- The grouting materials had to be resistant to salt and alkali and maintain functionality until the completion of underground structures.
- Adopt a two-stage grouting technique, initiating the reaction of the grout material at the grout pipe’s outlet, allowing better control of the setting time.
- The primary objective was water sealing, without excessively increasing soil compressive strength, to avoid additional time-consuming follow-up excavation.
—
3. Works Design
Based on the objectives outlined for the extensive bottom grouting and solution formulation, the works design was as follows:
1) Utilize the double-tube grouting method in conjunction with durable and alkali-resistant SSA chemical grout for ground improvement.
2) Employ a combination of instant setting grouting and delayed setting permeation to ensure uniform distribution of the grout within the improvement area.
3) Arrange the grouting holes in a staggered pattern with a spacing of 1.2m, effectively filling the loose soil zone.
4) The ground improvement to cover a depth range of GL-9.0m to GL-13.0m, targeting the lower edge of the steel sheet piles, the base level area, and the highly permeable soil layer below the excavation face.
5) Control parameters to include a step increment of 0.5m, a grout flow rate of approximately 12-14 L/min, and a final pressure not less than the initial pressure +200kPa. These conditions to allow the grout to permeate thoroughly into the soil.
6) After completion of the grouting, water discharge measurements combined with electrical resistivity probing to be used to verify the effectiveness of the bottom grouting.

—
4. Works Process
To facilitate the grouting work, a temporary PC layer was placed on the excavation face during construction.
This allowed for easier movement of the drilling machine and provided optimal conditions for operation, sampling, and drilling positioning. This approach helped prevent incomplete grout sealing due to drilling angles deviation.
During grouting, an instant setting chemical grout with a gelation time of 5-8 seconds was initially used to prevent grout-escape.
Subsequently, a combination of instant and delayed setting grout materials is employed, controlling the direction of grout diffusion and ensuring thorough penetration into the soil layers.

—
5. Results
During the grouting operation, as per the construction design, the water discharge gradually reduced, and effective control of water seepage was achieved by supplementing grouting in partially unsealed areas using spaced drilling method.
Upon completion of all the work, a water discharge verification was conducted, which met the standards for continuing with excavation.
Electrical resistivity probing within the improved area revealed no significant presence of abundant water or water pockets. Thus, the deep excavation bottom grouting in the coastal tidal zone had been successfully completed.

—
Base Level Grout Sealing of Deep Excavation in Coastal Tidal Zone
將下載檔案寄至:
・More Construction Result Sharing
Contact us:+886 2769-2355
Copyright ©Jines Construction Co.,Ltd