
SEALING TECHNOLOGY FOR FOUNDATION PIT EXCAVATION IN SEDIMENTARY STRATA
Rescue method for sealing foundation pit bottom after large water inrush emergency.
1. Project Background
A 10m-diameter shaft was being excavated by TBM for high-voltage underground cable on the Chidlom Station Outgoing Cable Tunnel Project in Bangkok, Thailand.
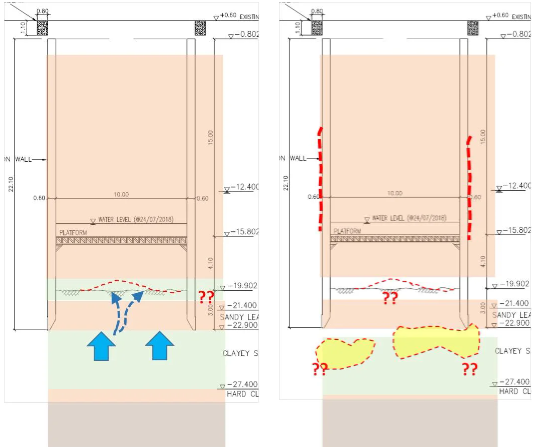
A sudden emergency occurred when the clay layer was broken through by upward force. A large amount of water and sand gushed out at the excavation surface, and the shaft sank by about 20 centimeters.
In order to avoid further expansion of the emergency, the construction unit injected emergency water into the shaft to maintain the water pressure balance.
This also reduced the continuous inrush of sand and soil that would cause the stratum to hollow out, and invited experts to discuss contingency countermeasures.
―
2. Solution
Jines (Thailand) Co., Ltd., a branch of the company in Thailand, immediately proposed two rescue solutions after being invited to participate in the emergency response meeting, these were:
(1) The enclosure water-stop scheme for the lower section of the shaft; and
(2) Shaft bottom sealing scheme.
After evaluating the repair time, cost and comprehensive benefits, a range of experts made the decision to use the shaft bottom sealing method to carry out water gushing emergency operations.
―
3. Work Design
According to the geological survey data, there was a sandy soil layer about 6 meters thick under a broken clay layer; the bottom of the layer being located at GL-28m.
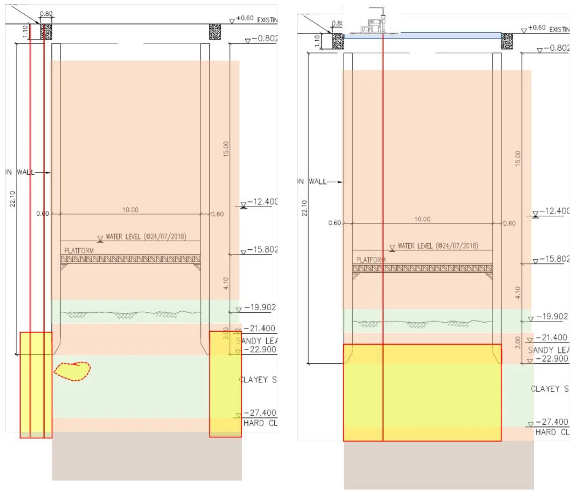
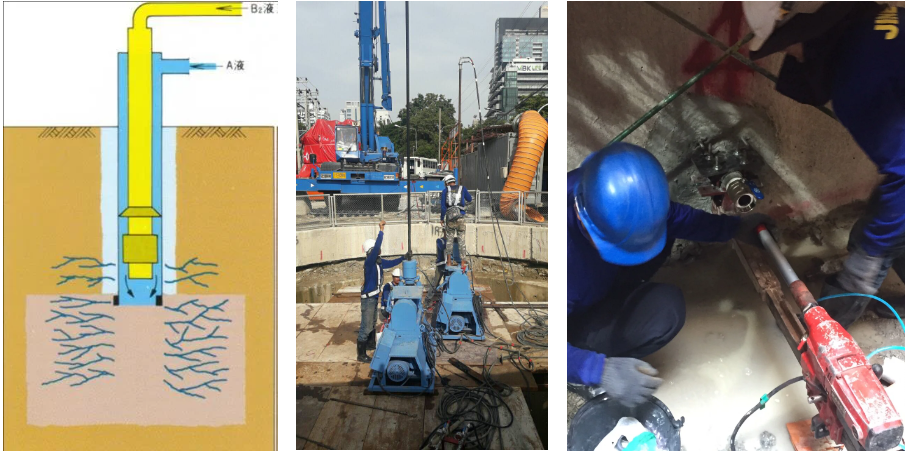
After analysis and calculations by our company, the recommendation was to use the double pipe grouting method with instant setting and quick setting chemical grout for vertical shaft bottom sealing grouting.
The pouring depth was 7m. The low-permeability clay below the sand layer was more than 1m deep.
In addition, after waiting for the water gushing in the vertical shaft to stop, perform horizontal grouting at the bottom of the excavation surface to ensure the water-stopping effect, and at the same time fully fill and reinforce the weak zones and holes in the disturbed strata.

―
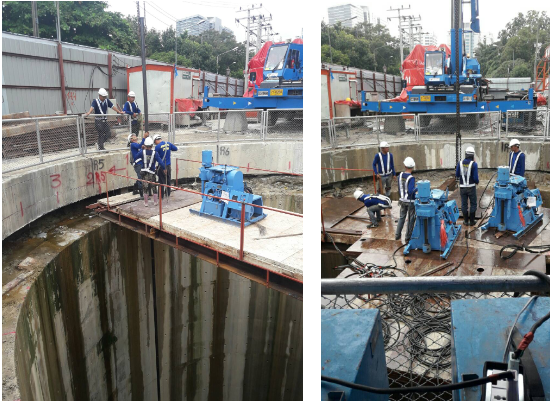
4. Work Process
During the pouring operation, it was found that there was a significant difference between the geological survey data of the base layer and the actual geological conditions.
In order to achieve a reliable bottom sealing effect, the actual pouring position was to penetrate the hard clay layer below the excavation surface to a depth of 1m.
In addition, reinforcement superimposed injection was carried out around the side wall of the shaft to ensure that the external water source would not enter the highly permeable sand layer below the shaft.

―
5. Results
After the chemical grout was poured, the water inrush at the bottom of the pit stopped completely, leaving only a small amount of water seepage.
The on-site water permeability test in the grouting area confirmed that the water permeability coefficient was less than 1×10-5cm/sec.
After reaching the conditions for excavation and concrete pouring, the construction unit rushed to complete the excavation of the foundation pit and laid the PC layer and tied the subslab of the shaft foundation.
Because of the secondary construction joints at the interface between the inner wall of the shaft and the foundation slab, there was a small amount of localized water seepage and dampness in the base slab after the concrete curing was completed.
The company prides itself on giving comprehensive service, so specially assigned professional engineers to carry out non-expanding PU resin leakage treatment by oblique holes in the construction joints.
Complete leakage prevention was achieved during the excavation of the bottom of the shaft and remained the same after the construction work was done.

―
Sealing Technology for Foundation Pit Excavation In Sedimentary Strata
將下載檔案寄至:
・More Construction Result Sharing
Contact us:+886 2769-2355
Copyright ©Jines Construction Co.,Ltd